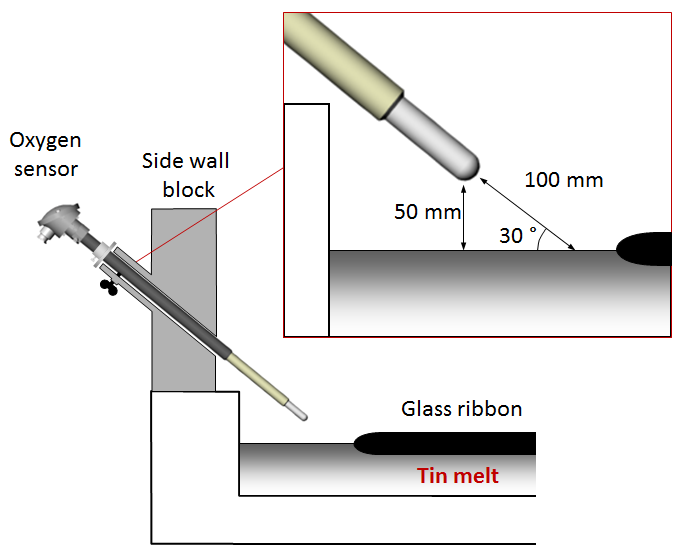
Under normal production conditions, the oxygen activity of the protective atmosphere is lower than that of the tin melt for an effective removal of oxygen from the tin melt. In this way the oxygen content of the tin melt can be kept low enough for defect free production. As most of the tin melt surface is covered by the glass ribbon, oxygen is more or less entrapped in the tin melt under the glass ribbon. Oxygen removal is a slow process, which can only take place via the small open space near the side walls of the bath.
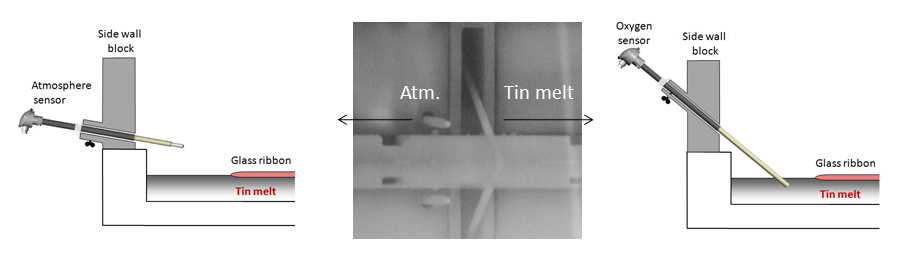
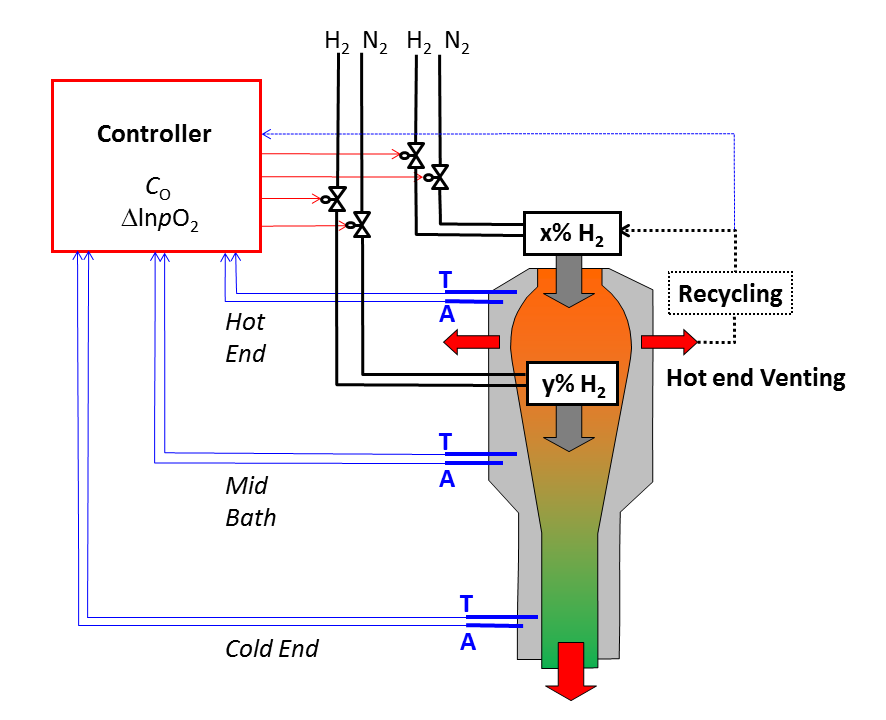
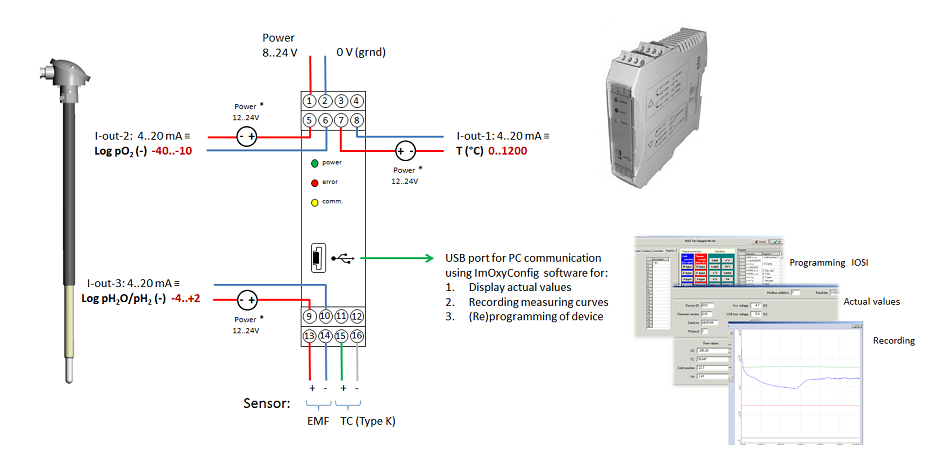
For this reason it is important to measure both the oxygen content of the tin melt and that of the atmosphere in various sections of the bath in order to maintain enough driving force for tin melt deoxidation along the entire length of the bath.
A detailed study on the behaviour of oxygen in the tin bath and the use of tin oxygen and atmosphere oxygen sensor pairs along the tin bath from hot end to cold end can be found in: Glass technol.: Eur. J. Glass Sic. Technol. A, December 2012, 53 (6), 261-272. This study was performed by the Asahi Glass Production Technology Center, using Read-Ox' tin bath oxygen sensors.

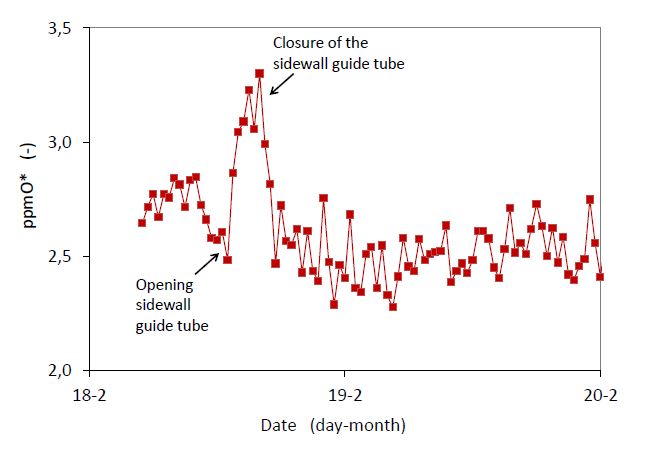 The Read-Ox tin bath atmosphere sensor, for measuring the oxygen activity of the protective atmosphere in the tin bath, is very sensitive to even the smallest amounts of oxygen leaking into the bath atmosphere. It is an ideal tool for indicating when sealing improvement activities are required or when an increase of the venting intensity and/or hydrogen supply to the bath is needed. Moreover, the sensor provides immediately feedback on the effectiveness of a specific sealing action.
The Read-Ox tin bath atmosphere sensor, for measuring the oxygen activity of the protective atmosphere in the tin bath, is very sensitive to even the smallest amounts of oxygen leaking into the bath atmosphere. It is an ideal tool for indicating when sealing improvement activities are required or when an increase of the venting intensity and/or hydrogen supply to the bath is needed. Moreover, the sensor provides immediately feedback on the effectiveness of a specific sealing action.